The Kentucky dataset is comprised of 18 real pipe systems throughout Kentucky and was created between 2014 and 2015. These systems were chosen to represent an array of looped, gridded, and branched networks. These systems have real world data associated with demand, water loss, and consumer cost of water.
Click the numbers below to jump to the corresponding systems.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
-
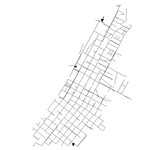
01 KY 1
The KY 1 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Hoagland in 2015 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.0 MGD, one reservoir, two tanks, and 40.6 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution sparse-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and gridded by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
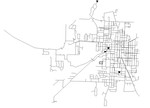
02 KY 2
The KY 2 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.09 MGD, one reservoir, three tanks, one pump, and 87.9 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution dense-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and gridded by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
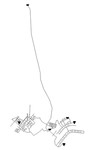
03 KY 3
The KY 3 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.02 MGD, three reservoirs, three tanks, five pump, and 52.5 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution dense-grid by Hwnag & Lansey (2017) and gridded by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
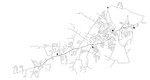
04 KY 4
The KY 4 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 1.51 MGD, one reservoir, four tanks, two pumps, and 162 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution sparse-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and looped by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
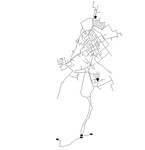
05 KY 5
The KY 5 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.28 MGD, four reservoirs, two tanks, nine pumps, and 52.3 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution sparse-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and looped by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
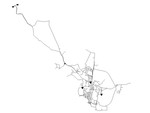
06 KY 6
The KY 6 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 1.56 MGD, two reservoirs, three tanks, two pumps, and 58.5 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution dense-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and looped by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
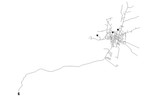
07 KY 7
The KY 7 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 1.53 MGD, one reservoir, three tanks, one pump, and 79.3 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution dense-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and gridded by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
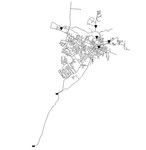
08 KY 8
The KY 8 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.47 MGD, two reservoirs, five tanks, four pumps, and 150 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution sparse-grid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and looped by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
09 KY 9
The KY 9 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 1.38 MGD, four reservoirs, 15 tanks, 17 pumps, and 594 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution branch by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and branched by Hoagland et al. (2015).
-
10 KY 10
The KY 10 system is based on a real-world system in KY and was originally used by Jolly et al. in 2014 as part of a classification study. The system has a total demand of 2.26 MGD, two reservoirs, 13 tanks, 13 pumps, and 256 miles of pipe. It is classified as distribution hybrid by Hwang & Lansey (2017) and gridded by Hoagland et al. (2015).

